These charts are your go-to resource for finding the perfect fit across a variety of apparel and footwear. They are designed to help both shoppers and retailers by simplifying the sizing process, ensuring you select the correct size on your first try. This is crucial for online shopping, where trying items on isn’t an option.
- Shoe Sizes
- Children’s Shoe Sizes
- Jeans and Pants Sizes
- Women’s Clothes Sizes
- Men’s Clothes Sizes
- Children’s Sizes
The charts take into account the differences in body shapes and sizes, aiming to provide a comfortable and flattering fit for everyone. By reducing the guesswork in sizing, these charts improve shopping experiences and minimize returns, making shopping more efficient and satisfying.

Step Conversion
| Steps | Miles (males) | Miles (females) |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 0.49 | 0.41 |
| 2,000 | 0.98 | 0.82 |
| 2,500 | 1.23 | 1.03 |
| 3,000 | 1.7 | 1.23 |
| 5,000 | 2.45 | 2.05 |
| 6,000 | 2.94 | 2.46 |
| 7,500 | 3.67 | 3.08 |
| 10,000 | 4.91 | 4.10 |
| 15,000 | 7.36 | 6.15 |
| 20,000 | 9.82 | 8.20 |
| 21,000 | 10.31 | 8.61 |
Our step conversion chart is a practical tool for translating the number of steps you take into miles, with separate conversions for males and females to account for the average stride length differences between genders. For example, it tells you exactly how far 10,000 steps are in miles and provides the conversions for a range of step counts, such as how many miles 6,000 steps equate to.

This chart is incredibly useful for setting and tracking fitness goals. It helps you understand the distance you’ve covered during your walks or runs, encouraging you to achieve your daily step targets. Whether you’re aiming for 10,000 steps a day or setting a personal goal of 15,000 steps, this chart makes it clear how much ground you’re covering, aiding in planning and motivation.
Pixel Conversion
| Size Type | Dimensions (Inches) | Dimensions (cm) | Pixels at 72 DPI | Pixels at 300 DPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US Letter | 8.5 x 11 | 21.59 x 27.94 | 612 x 792 | 2550 x 3300 |
| US Legal | 8.5 x 14 | 21.59 x 35.56 | 612 x 1008 | 2550 x 4200 |
| US Tabloid | 11 x 17 | 27.94 x 43.18 | 792 x 1224 | 3300 x 5100 |
| Euro DIN A4 | 8.27 x 11.7 | 21 x 29.7 | 595 x 842 | 2481 x 3510 |
| Euro DIN A3 | 11.7 x 16.5 | 29.7 x 42 | 842 x 1188 | 3510 x 4950 |
| Euro DIN A2 | 16.5 x 23.4 | 42 x 59.4 | 1188 x 1684 | 4950 x 7020 |
The Pixel Conversion Chart is essential for anyone working with digital or print media, converting dimensions in inches and centimeters into pixels at 72 DPI (for web) and 300 DPI (for print). This differentiation is key because the resolution impacts how clear an image will appear in different formats. For instance, designers can use this chart to ensure that a digital design will look crisp both on a computer screen and when printed.

It facilitates precise planning for projects requiring size-specific designs, such as posters, business cards, or website elements, ensuring your work meets industry standards for clarity and detail.
Ergonomic Heights for Chairs, Tables, and Countertops
| Item | Optimal Height for Women (cm) | Optimal Height for Women (inches) | Optimal Height for Men (cm) | Optimal Height for Men (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chair (Normal Seating) | 38-45 | 15-17.7 | 40-47 | 15.7-18.5 |
| Chair (Office Seating) | 42-50 | 16.5-19.7 | 44-52 | 17.3-20.5 |
| Dining Table | 72-75 | 28.3-29.5 | 74-77 | 29.1-30.3 |
| Office Table | 72-75 | 28.3-29.5 | 74-77 | 29.1-30.3 |
| Kitchen Countertop | 85-90 | 33.5-35.4 | 90-95 | 35.4-37.4 |
| Bathroom Countertop | 80-85 | 31.5-33.5 | 85-90 | 33.5-35.4 |
| Workbench | 85-90 | 33.5-35.4 | 90-95 | 35.4-37.4 |
This table offers guidance on the optimal heights for chairs, tables, and countertops to ensure ergonomic comfort for both women and men. It recognizes the physical differences between genders, such as average height and body proportions, to suggest furniture heights that reduce strain and enhance comfort in various settings, from the office to the kitchen.
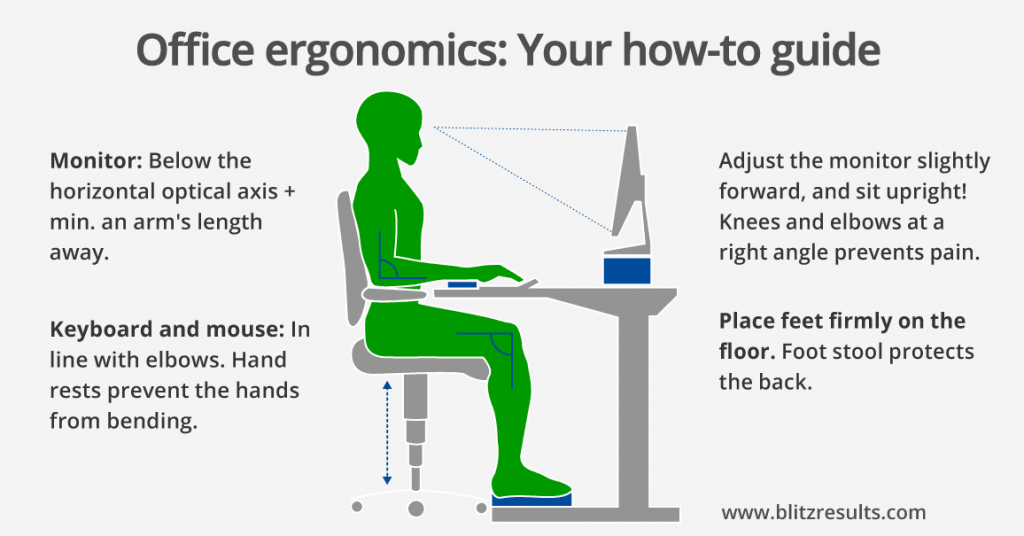
Following these recommendations can help prevent discomfort and long-term health issues associated with poor posture, making it valuable for anyone looking to furnish their space with health and comfort in mind.
Standard Meat Serving per Person
| Number of Persons | Total Meat Serving for Men (oz) | Total Meat Serving for Men (g) | Total Meat Serving for Women (oz) | Total Meat Serving for Women (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | 227 | 6 | 170 |
| 2 | 16 | 454 | 12 | 340 |
| 3 | 24 | 680 | 18 | 510 |
| 4 | 32 | 907 | 24 | 680 |
This chart provides a guideline for meat servings per person, distinguishing between men and women to reflect the general differences in dietary needs and portion sizes. It’s particularly useful for anyone planning meals, whether you’re cooking at home or planning a menu for a restaurant.

The chart helps ensure that servings are appropriate for the dietary needs of your guests, promoting healthy eating habits and reducing food waste. By adjusting servings according to these guidelines, you can cater to your nutritional requirements while managing resources efficiently.
Toilet Paper Consumption
| Number of Persons | US Consumption (rolls/year) | Europe Consumption (rolls/year) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 140 | 100 |
| 2 | 280 | 200 |
| 3 | 420 | 300 |
| 4 | 560 | 400 |
This comparison sheds light on the varying habits of toilet paper consumption between the US and Europe, influenced by roll size, sheet size, consumer habits, and cultural preferences. The differences in gender and measurement systems highlight how consumption can vary not just between regions but within households, reflecting personal preferences, environmental concerns, and cultural practices.
This information can guide consumers in making more sustainable choices and help manufacturers tailor their products to different markets, balancing consumer preferences with environmental impact.
